This gearmotor is a compact (1.50" x 0.59" x 0.47") brushed DC motor with 35:1 metal gearbox. These units have a 0.365"-long, 3 mm-diameter D-shaped output shaft that matches the micro metal gearmotor output shafts. Key specs at 6 V: 350 RPM and 70 mA free-run, 20 oz-in (1.4 kg-cm) and 1.5 A stall.
This brushed DC motor has a long (0.365" or 9.27 mm, not 8mm as shown in the drawing below), 3 mm-diameter D-shaped metal output shaft that matches our assortment of Pololu wheels and the Solarbotics RW2 rubber wheel. Alternatively, you can use the Pololu universal mounting hub to mount custom wheels and mechanism to the micro metal gearmotor’s output shaft, and you can use our 12mm hex wheel adaptor to use this motor with many common hobby RC wheels.
The brass faceplate has two mounting holes threaded for M2 screws (2 mm diameter, 0.4 mm thread pitch). This gearmotor works with our 15.5D mm metal gearmotor brackets.
Note: this gearmotor is not compatible with our Sanyo-style micro gearmotor mounting brackets (products 989 and 1089).
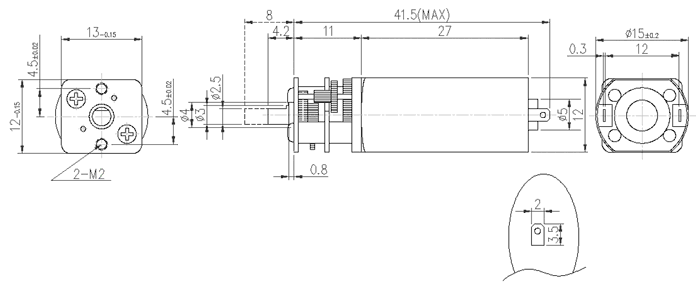 |
| 35:1 mini metal gearmotor dimensions (units in mm). |
|---|
These motors are intended for use at 9 V, which means you can get more speed and torque out of this motor than is listed in the 6 V specs. In general, these kinds of motors can run at voltages above and below this nominal voltage, so they should comfortably operate in the 3 – 12 V range (the motor can begin rotating at voltages as low as 0.5 V). Lower voltages might not be practical, and higher voltages could start negatively affecting the life of the motor.
At 6 V, this gearmotor will have a no-load RPM of around 350 with a free-run current of 70 mA, a stall current of 1.5 A, and a stall torque of around 14 oz-in (1 kg-cm).
We offer a wide selection of metal gearmotors that offer different combinations of speed and torque. Our metal gearmotor comparison table can help you find the motor that best meets your project’s requirements.
 |
| Some of the Pololu metal gearmotors. |
|---|
| Size: | 38 x 12 x 15 mm |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 23 g |
| Shaft diameter: | 3 mm |
| Gear ratio: | 35:1 |
|---|---|
| Free-run speed @ 6V: | 350 rpm |
| Free-run current @ 6V: | 70 mA |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 1500 mA |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 20 oz·in |
No; the information we have available for this motor can be found on its product page. However, you can approximate various additional motor parameters from the information found in the “Specs” tab.
The electrical resistance of the motor can be approximated by dividing the rated voltage by the stall current (at the rated voltage). The electromotive force constant (Ke) can be approximated by dividing the rated voltage by the free-run speed (at the rated voltage). To approximate the motor torque constant (Kt), you can divide the stall torque by the stall current.
For pretty much any DC motor, the current, speed, power, and efficiency curves as a function of torque will look like those in the graph below (assuming motor voltage and temperature are constant):
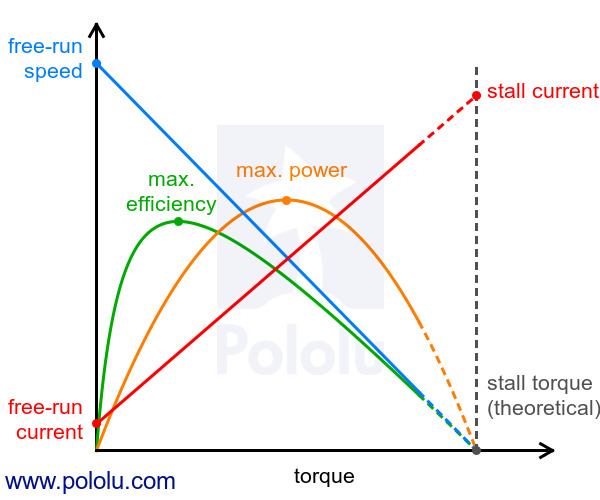 |
The current and speed curves are approximately linear, and the product pages for our motors provide the approximate end points for these lines: (0 torque, no-load current) and (stall torque, stall current) for the red line, and (0 torque, no-load speed) and (stall torque, 0 speed) for the blue line.
The orange output power curve is the product of the speed and the torque, which results in an inverted parabola with its peak at 50% of the stall torque.
The green efficiency curve is the output power divided by the input power, where the input power is current times voltage. The voltage is constant, so you can divide the output power curve by the current line to get the general shape of the efficiency curve, which in turn lets you identify the torque, speed, and current that correspond to max efficiency.
There are many programs out there that you can use to generate these curves. For example, if you have access to MATLAB, you can use this customer-created MATLAB script to generate these motor plots for you from the specifications we provide for each gearmotor.
Note: A good general rule of thumb is to keep the continuous load on a DC motor from exceeding approximately 20% to 30% of the stall torque. Stalling gearmotors can greatly decrease their lifetimes, occasionally resulting in immediate damage to the gearbox or thermal damage to the motor windings or brushes. Do not expect to be able to safely operate a brushed DC gearmotor all the way to stall. The safe operating range will depend on the specifics of the gearmotor itself.