This is the motor and encoder portion of our high-power (HP), 6V 25D mm metal gearmotors with 48 CPR encoders.
Special Order
Shipping from $9.90
+61 more from our supplier in 7-10 days
Our Code: SKU-005609
Supplier Link: [Pololu MPN:4800]
This is the motor and encoder portion of our high-power (HP), 6V 25D mm metal gearmotors with 48 CPR encoders. It does not include a gearbox, but the pinion gear on the output shaft works with all of our 25D mm gearmotor gearboxes, so this can be used as a replacement motor or encoder for those gearboxes.
Key specifications:
| voltage | no-load performance | stall extrapolation |
|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 10000 RPM, 500 mA | 0.3 kg⋅cm (4 oz⋅in), 6.0 A |
  |
This motor with integrated 48 CPR (counts per revolution) quadrature encoder is intended as a replacement high-power (HP) 6 V motor with encoder for our 25D mm metal gearmotors. It is intended for use at 6 V, but in general, these kinds of motors can run at voltages above and below this nominal voltage. Lower voltages might not be practical, and higher voltages could start negatively affecting the life of the motor.
The output shaft has a non-removable pinion gear that works with all of our 25D mm gearmotor gearboxes. Note that we do not sell the 25D mm gearboxes separately, but if you have a gearmotor with a damaged motor or encoder (or if you want to effectively add an encoder to a version without an encoder), you can transfer the gearbox to this replacement motor.
The motor has a diameter of 24.2 mm (0.95 in) and a length of approximately 43 mm (1.7 in) from the top of the motor can to the bottom of the encoder. The top of the motor has two mounting holes threaded for M3 screws. These mounting holes are 17 mm apart and form a line with the motor shaft at the centre. The mounting holes have a depth of approximately 2 mm.
Other motor windings with identical dimensions and pinion gears are also available, resulting in five total options:
These motors are functionally identical to the previous versions we carried without end caps (they use the same motor and encoder). The black plastic end cap is easily removable if you need to access the encoder or want to slightly reduce the overall motor size, but there is a little bit of base plastic that will remain, as shown in the picture below:
You will typically want to combine this motor with a gearbox to give it a more appropriate combination of torque and speed (without a gearbox, it offers very high speed with very low torque). The HP 6V versions of our 25D mm metal gearmotors consist of this motor combined with different gearboxes. We do not carry the gearboxes by themselves, so unless you are looking at this as a replacement motor for a compatible gearbox you already have, we strongly recommend you consider getting a preassembled gearmotor with the gear ratio that best suits your project requirements.
| Rated Voltage |
Motor Type |
Stall Current |
No-Load Current |
Gear Ratio | No-Load Speed (RPM) |
Extrapolated Stall Torque |
Max Power (W) |
 Without Encoder |
 With Encoder |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kg ⋅ cm) | (oz ⋅ in) | |||||||||
| 12 V | High-Power (HP) |
5.0 A | 250 mA w/o encoder 300 mA with encoder |
1:1 (no gearbox) | 10,000 | 0.4 | 5.5 | 10 | – | item #4840 |
| 4.4:1 | 2200 | 1.7 | 24 | 9.4 | item #3201 | item #4841 | ||||
| 9.7:1 | 1000 | 3.9 | 54 | 10 | item #3202 | item #4842 | ||||
| 20.4:1 | 500 | 7.4 | 100 | 9.4 | item #3203 | item #4843 | ||||
| 34:1 | 300 | 11 | 150 | 8.9 | item #3204 | item #4844 | ||||
| 47:1 | 220 | 15 | 210 | 8.4 | item #3205 | item #4845 | ||||
| 75:1 | 130 | 22 | 310 | – | item #3206 | item #4846 | ||||
| 99:1 | 100 | 29 | 400 | – | item #3207 | item #4847 | ||||
| 12 V | Medium-Power (MP) |
1.8 A | 80 mA w/o encoder 100 mA with encoder |
1:1 (no gearbox) | 8200 | 0.17 | 2.4 | 3.5 | – | item #4860 |
| 4.4:1 | 1800 | 0.71 | 10 | 3.2 | item #3225 | item #4861 | ||||
| 9.7:1 | 800 | 1.7 | 24 | 3.4 | item #3226 | item #4862 | ||||
| 20.4:1 | 380 | 3.2 | 44 | 3.1 | item #3227 | item #4863 | ||||
| 34:1 | 230 | 4.7 | 65 | 2.8 | item #3228 | item #4864 | ||||
| 47:1 | 170 | 6.4 | 89 | 2.8 | item #3229 | item #4865 | ||||
| 75:1 | 100 | 8.5 | 120 | 2.3 | item #3230 | item #4866 | ||||
| 99:1 | 79 | 11 | 150 | 2.3 | item #3231 | item #4867 | ||||
| 172:1 | 46 | 18 | 250 | 2.1 | item #3232 | item #4868 | ||||
| 227:1 | 35 | 24 | 330 | – | item #3233 | item #4869 | ||||
| 12 V | Low-Power (LP) |
0.9 A | 50 mA w/o encoder 60 mA with encoder |
1:1 (no gearbox) | 5600 | 0.14 | 1.9 | 1.8 | – | item #4880 |
| 4.4:1 | 1200 | 0.53 | 7.4 | 1.7 | item #3249 | item #4881 | ||||
| 9.7:1 | 580 | 1.3 | 18 | 1.8 | item #3250 | item #4882 | ||||
| 20.4:1 | 280 | 2.4 | 33 | 1.7 | item #3251 | item #4883 | ||||
| 34:1 | 170 | 3.7 | 51 | 1.6 | item #3252 | item #4884 | ||||
| 47:1 | 120 | 4.8 | 67 | 1.4 | item #3253 | item #4885 | ||||
| 75:1 | 75 | 7.1 | 99 | 1.4 | item #3254 | item #4886 | ||||
| 99:1 | 57 | 8.7 | 120 | 1.2 | item #3255 | item #4887 | ||||
| 172:1 | 33 | 13 | 180 | 1.1 | item #3256 | item #4888 | ||||
| 227:1 | 25 | 16 | 220 | 1.0 | item #3257 | item #4889 | ||||
| 378:1 | 15 | 23 | 320 | – | item #3258 | item #4890 | ||||
| 6 V | High-Power (HP) |
6.0 A | 420 mA w/o encoder 500 mA with encoder |
1:1 (no gearbox) | 10,000 | 0.3 | 4 | 7 | – | item #4800 |
| 4.4:1 | 2200 | 1.2 | 17 | 6.7 | item #1570 | item #4801 | ||||
| 9.7:1 | 1000 | 2.3 | 32 | 5.9 | item #1571 | item #4802 | ||||
| 20.4:1 | 480 | 4.8 | 67 | 5.9 | item #1572 | item #4803 | ||||
| 34:1 | 290 | 6.8 | 94 | 5.1 | item #1573 | item #4804 | ||||
| 47:1 | 210 | 9.1 | 130 | 4.9 | item #1574 | item #4805 | ||||
| 75:1 | 130 | 14 | 190 | 4.5 | item #1575 | item #4806 | ||||
| 99:1 | 99 | 15 | 210 | 3.9 | item #1576 | item #4807 | ||||
| 172:1 | 57 | 27 | 380 | – | item #1577 | item #4808 | ||||
| 6 V | Low-Power (LP) |
2.0 A | 100 mA w/o encoder 120 mA with encoder |
1:1 (no gearbox) | 6200 | 0.15 | 2.1 | 2.1 | – | item #4820 |
| 4.4:1 | 1300 | 0.63 | 8.7 | 2.1 | item #1581 | item #4821 | ||||
| 9.7:1 | 630 | 1.3 | 18 | 1.9 | item #1582 | item #4822 | ||||
| 20.4:1 | 290 | 2.5 | 35 | 1.9 | item #1583 | item #4823 | ||||
| 34:1 | 180 | 3.9 | 54 | 1.7 | item #1584 | item #4824 | ||||
| 47:1 | 130 | 4.8 | 67 | 1.5 | item #1585 | item #4825 | ||||
| 75:1 | 80 | 7.5 | 100 | 1.5 | item #1586 | item #4826 | ||||
| 99:1 | 61 | 9.1 | 130 | 1.4 | item #1587 | item #4827 | ||||
| 172:1 | 35 | 14 | 190 | 1.2 | item #1588 | item #4828 | ||||
| 227:1 | 27 | 17 | 240 | 1.1 | item #1589 | item #4829 | ||||
| 378:1 | 16 | 25 | 350 | – | item #1590 | item #4830 | ||||
| 499:1 | 12 | 31 | 430 | – | item #1591 | item #4831 | ||||
Note: The listed stall torques and currents are theoretical extrapolations; units will typically stall well before these points as the motors heat up. Stalling or overloading gearmotors can greatly decrease their lifetimes and even result in immediate damage. The recommended upper limit for continuously applied loads is 4 kg⋅cm (55 oz⋅in), and the recommended upper limit for intermittently permissible torque is 8 kg⋅cm (110 oz⋅in). Stalls can also result in rapid (potentially on the order of seconds) thermal damage to the motor windings and brushes; a general recommendation for brushed DC motor operation is 25% or less of the stall current.
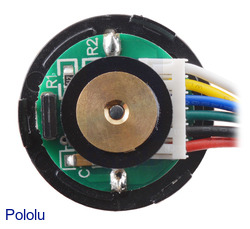  |
25D mm metal gearmotor with 48 CPR encoder (with end cap removed). |
|---|
The 25D and 37D mm metal gearmotors with encoders have cables that are terminated with a 6-pin, 0.1″-pitch female connector.
A two-channel Hall effect encoder is used to sense the rotation of a magnetic disk on a rear protrusion of the motor shaft. The quadrature encoder provides a resolution of 48 counts per revolution of the motor shaft when counting both edges of both channels. To compute the counts per revolution of the gearbox output, multiply the gear ratio by 48. The motor/encoder has six colour-coded, 11" (28 cm) leads terminated by a 1×6 female header with a 0.1″ pitch, as shown in the main product picture. This header works with standard 0.1″ male headers and our male jumper and precrimped wires. If this header is not convenient for your application, you can pull the crimped wires out of the header or cut the header off. The following table describes the wire functions:
| Colour | Function |
|---|---|
| Red | motor power (connects to one motor terminal) |
| Black | motor power (connects to the other motor terminal) |
| Green | encoder GND |
| Blue | encoder Vcc (3.5 – 20 V) |
| Yellow | encoder A output |
| White | encoder B output |
The Hall sensor requires an input voltage, Vcc, between 3.5 and 20 V and draws a maximum of 10 mA. The A and B outputs are square waves from 0 V to Vcc approximately 90° out of phase. The frequency of the transitions tells you the speed of the motor, and the order of the transitions tells you the direction. The following oscilloscope capture shows the A and B (yellow and white) encoder outputs using a motor voltage of 6 V and a Hall sensor Vcc of 5 V:
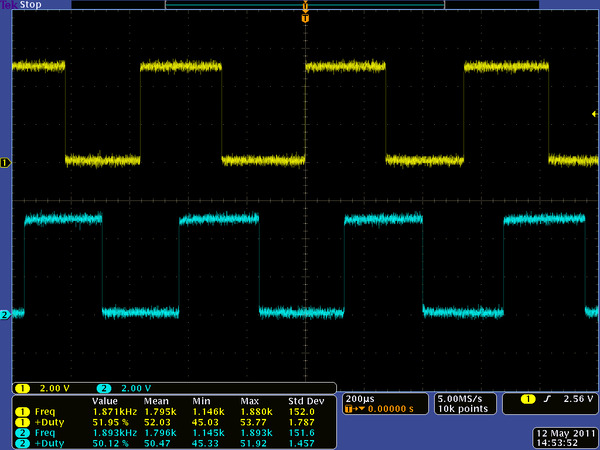 |
Encoder A and B outputs for 25D mm HP 6V metal gearmotor with 48 CPR encoder (motor running at 6 V). |
|---|
By counting both the rising and falling edges of both the A and B outputs, it is possible to get 48 counts per revolution of the motor shaft. Using just a single edge of one channel results in 12 counts per revolution of the motor shaft, so the frequency of the A output in the above oscilloscope capture is 12 times the motor rotation frequency.
We offer a wide selection of metal gearmotors that offer different combinations of speed and torque. Our metal gearmotor comparison table can help you find the motor that best meets your project’s requirements.
 |
| Size: | 25D x 46L mm1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 60 g |
| Gear ratio: | 1:12 |
|---|---|
| No-load speed @ 6V: | 10000 rpm3 |
| No-load current @ 6V: | 0.50 A4 |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 6.0 A5 |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 0.3 kg·cm5 |
| Max output power @ 6V: | 7 W |
| Motor type: | 6V, 6.0A stall (HP 6V) |
| Lead length: | 8 in6 |
| Encoders?: | Y |
This file contains 3D models (in the step file format) of the 25D mm gearmotors with and without encoders.
No! Stalls can result in rapid (potentially on the order of seconds) thermal damage to the motor windings and brushes; a general recommendation for brushed DC motor operation is 25% or less of the stall current, which means keeping continuously applied loads around 25% or less of the stall torque.
Additionally, for many of our gearmotors with high gear ratios, the extrapolated stall torque is beyond what the gearboxes are designed to handle, and a stall could instantly damage the gears. Make sure to keep applied loads within the published limits for your gearmotor.