This version of our DRV8825 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier ships with male header pins installed , so no soldering is required to use it with an appropriate 16-pin socket or solderless breadboard. Please see the DRV8825 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier product page for more information about the driver.
In stock in Australia
Shipping from $7.90
+123 more from our supplier in 7-10 days
Our Code: SKU-003467
Supplier Link: [Pololu MPN:2982]
This version of our DRV8825 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier ships with 0.1″-pitch male header pins installed as shown in the main product picture, so no soldering is required to use it with an appropriate 16-pin socket or solderless breadboard. Please see the DRV8825 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier product page for more information about the driver.
| Size: | 0.6″ × 0.8″ |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 2.7 g |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 8.2 V |
|---|---|
| Maximum operating voltage: | 45 V |
| Continuous current per phase: | 1.5 A1 |
| Maximum current per phase: | 2.2 A2 |
| Minimum logic voltage: | 2.5 V3 |
| Maximum logic voltage: | 5.25 V3 |
| Microstep resolutions: | full, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32 |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | N |
| Bulk packaged: | N |
| Header pins soldered: | Y |
Yes. To avoid damaging your stepper motor, you want to avoid exceeding the rated current, which is 600 mA in this instance. The DRV8825 stepper motor drivers let you limit the maximum current, so as long as you set the limit below the rated current, you will be within spec for your motor, even if the voltage exceeds the rated voltage. The voltage rating is just the voltage at which each coil draws the rated current, so the coils of your stepper motor will draw 600 mA at 3.9 V. By using a higher voltage along with active current limiting, the current is able to ramp up faster, which lets you achieve higher step rates than you could using the rated voltage.
If you do want to use a lower motor supply voltage (under 8 V) for other reasons, consider using our DRV8834 low-voltage stepper motor driver carrier.
Yes, you do! Setting the current limit on your stepper motor driver carrier before connecting your motor is essential to making sure that it runs properly. An appropriate current limit also ensures that your motor is not allowed to draw more current than it or your driver can handle, since that is likely to damage one or both of them.
Setting the current limit on our A4988, DRV8825, DRV8824, DRV8834, and DRV8880 stepper motor driver carriers is done by adjusting the on-board potentiometer. We strongly recommend using a multimeter to measure the VREF voltage while setting the current limit so you can be sure you set it to an appropriate value (just turning the pot randomly until things seem to work is not a good approach). The following video has more details on setting the current limit:
Measuring the current draw at the power supply does not necessarily provide an accurate measure of the coil current. Since the input voltage to the driver can be significantly higher than the coil voltage, the measured current on the power supply can be quite a bit lower than the coil current (the driver and coil basically act like a switching step-down power supply). Also, if the supply voltage is very high compared to what the motor needs to achieve the set current, the duty cycle will be very low, which also leads to significant differences between average and RMS currents: RMS current is what is relevant for power dissipation in the chip but many power supplies won’t show that. You should base your assessment of the coil current on the set current limit or by measuring the actual coil currents.
Please note that while the DRV8825 driver IC is rated for up to 2.5 A per coil, the 0.5 W current sense resistors are only rated for 2.2 A, and the chip by itself will overheat at lower currents. We have found that it generally requires a heat sink to deliver more than approximately 1.5 A per coil, but this number depends on factors such as ambient temperature and air flow. For example, sealing three DRV8825 driver carriers in close proximity in a small box will cause them to overheat at lower currents than a unit by itself in open air.
The answer to this question depends on the type of stepper motor you have. When working with stepper motors, you will typically encounter two types: unipolar stepper motors and bipolar stepper motors. Unipolar motors have two windings per phase, allowing the magnetic field to be reversed without having to reverse the direction of current in a coil, which makes unipolar motors easier to control than bipolar stepper motors. The drawback is that only half of the phase is carrying current at any given time, which decreases the torque you can get out of the stepper motor. However, if you have the appropriate control circuitry, you can increase the stepper motor torque by using the unipolar stepper motor as a bipolar stepper motor (note: this is only possible with 6- or 8-lead unipolar stepper motors, not with 5-lead unipolar stepper motors). Unipolar stepper motors typically have five, six, or eight leads.
Bipolar steppers have a single coil per phase and require more complicated control circuitry (typically an H-bridge for each phase). The DRV8824/DRV8825 has the circuitry necessary to control a bipolar stepper motor. Bipolar stepper motors typically have four leads, two for each coil.
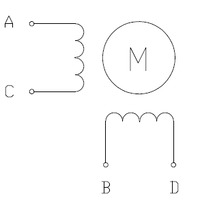 |
| Two-phase bipolar stepper motor with four leads. |
|---|
The above diagram shows a standard bipolar stepper motor. To control this with the DRV8824/DRV8825, connect stepper lead A to board output A1, stepper lead C to board output A2, stepper lead B to board output B1, and stepper lead D to board output B2. See the DRV8824 or DRV8825 datasheet for more information.
If you have a six-lead unipolar stepper motor as shown in the diagram below:
 |
| Two-phase unipolar stepper motor with six leads. |
|---|
you can connect it to the DRV8824/DRV8825 as a bipolar stepper motor by making the bipolar connections described in the section above and leaving stepper leads A’ and B’ disconnected. These leads are centre taps to the two coils and are not used for bipolar operation.
If you have an eight-lead unipolar stepper motor as shown in the diagram below:
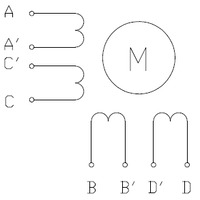 |
| Two-phase unipolar stepper motor with eight leads. |
|---|
you have several connection options. An eight-lead unipolar stepper motor has two coils per phase, and it gives you access to all of the coil leads (in a six-lead unipolar motor, lead A’ is internally connected to C’ and lead B’ is internally connected to D’). When operating this as a bipolar stepper, you have the option of using the two coils for each phase in parallel or in series. When using them in parallel, you decrease coil inductance, which can lead to increased performance if you have the ability to deliver more current. However, since the DRV8824/DRV8825 actively limits the output current per phase, you will only get half the phase current flowing through each of the two parallel coils. When using them in series, it’s like having a single coil per phase (like in four-lead bipolar steppers or six-lead unipolar steppers used as bipolar steppers). We recommend you use a series connection.
To connect the phase coils in parallel, connect stepper leads A and C’ to board output A1, stepper leads A’ and C to board output A2, stepper leads B and D’ to board output B1, and stepper leads B’ and D to board output B2.
To connect the phase coils in series, connect stepper lead A’ to C’ and stepper lead B’ to D’. Stepper leads A, C, B, and D should be connected to the stepper motor driver as normal for a bipolar stepper motor (see the bipolar stepper connections above).