This gearmotor is a miniature medium-power, 6 V brushed DC motor with a 4.995:1 metal gearbox. It has a cross section of 10 × 12 mm, and the D-shaped gearbox output shaft is 9 mm long and 3 mm in diameter. Key specs at 6 V: 4400 RPM and 40 mA with no load, 1.5 oz-in (0.1 kg-cm) and 0.7 A at stall.
Special Order
Shipping from $7.90
+129 more from our supplier in 7-10 days
Our Code: SKU-004604
Supplier Link: [Pololu MPN:2362]
These tiny brushed DC gearmotors are available in a wide range of gear ratios—from 5:1 up to 1000:1—and with five different motors: high-power 6 V and 12 V motors with long-life carbon brushes (HPCB), and high-power (HP), medium power (MP), and low power (LP) 6 V motors with shorter-life precious metal brushes. The 6 V and 12 V HPCB motors offer the same performance at their respective nominal voltages, just with the 12 V motor drawing half the current of the 6 V motor. The 6 V HPCB and 6 V HP motors are identical except for their brushes, which only affect the lifetime of the motor.
The HPCB versions (shown on the left in the picture below) can be differentiated from versions with precious metal brushes (shown on the right) by their copper-coloured terminals. Note that the HPCB terminals are 0.5 mm wider than those on the other micro metal gearmotor versions (2 mm vs. 1.5 mm), and they are about 1 mm closer together (6 mm vs. 7 mm).
Micro metal gearmotor HPCB with long-life carbon brushes (left) next to one with precious metal brushes.
Micro metal gearmotor HPCB long-life carbon brushes (left) next to micro metal gearmotor HP precious metal brushes (right).
Versions of these gearmotors are also available with an additional 1 mm-diameter output shaft that protrudes from the rear of the motor. This 4.5 mm-long rear shaft rotates at the same speed as the input to the gearbox and offers a way to add an encoder, such as our magnetic encoder for micro metal gearmotors (see the picture on the right), to provide motor speed or position feedback.
With the exception of the 1000:1 gear ratio versions, all of the micro metal gearmotors have the same physical dimensions, so one version can be easily swapped for another if your design requirements change. Please see the micro metal gearmotor comparison table for detailed specifications of all our micro metal gearmotors. This dynamically-sortable table can help you find the gearmotor that offers the best blend of speed, torque, and current-draw for your particular application. A more basic comparison table is available below.
Note: Stalling or overloading gearmotors can greatly decrease their lifetimes and even result in immediate damage. The recommended upper limit for instantaneous torque is 35 oz-in (2.5 kg-cm) for the 1000:1 gearboxes and 25 oz-in (2 kg*cm) for all the other gear ratios; we strongly advise keeping applied loads well under this limit. Stalls can also result in rapid (potentially on the order of seconds) thermal damage to the motor windings and brushes, especially for the versions that use high-power (HP and HPCB) motors; a general recommendation for brushed DC motor operation is 25% or less of the stall current.
In general, these kinds of motors can run at voltages above and below their nominal voltages; lower voltages might not be practical, and higher voltages could start negatively affecting the life of the motor.
Exact gear ratio: ``(27×37) / (20×10) =bb(4.995:1)``
In terms of size, these gearmotors are very similar to Sanyo’s popular 12 mm NA4S DC gearmotors, and gearmotors with this form factor are occasionally referred to as N20 motors. The versions with carbon brushes (HPCB) have slightly different terminal and end-cap dimensions than the versions with precious metal brushes, but all of the other dimensions are identical.
Dimensions of the Pololu micro metal gearmotors with carbon brushes (HPCB). Units are mm over [inches].
Dimensions of the Pololu micro metal gearmotors with precious metal brushes: low-power (LP), medium-power (MP), and high-power (HP). Units are mm over [inches].
These diagrams are also available as a downloadable PDF (262k pdf).
|
|
|
|
Note: The HPCB versions of our micro metal gearmotors are not compatible with our #2590 and #2591 optical encoders or our older #2598 magnetic encoders (the terminals are too wide to fit through the corresponding holes in the encoder boards). However, they are compatible with our newer #3081 magnetic encoders.
|
|
|
|
|
We also incorporate these motors into some of our products, including our Zumo robot and 3pi robot :
|
|
We offer a wide selection of metal gearmotors that offer different combinations of speed and torque. Our metal gearmotor comparison table can help you find the motor that best meets your project’s requirements.
 |
Some of the Pololu metal gearmotors. |
|---|
| Size: | 10 × 12 × 26 mm |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 9.5 g |
| Shaft diameter: | 3 mm1 |
| Gear ratio: | 4.995:1 |
|---|---|
| Free-run speed @ 6V: | 4400 Gbytes |
| Free-run current @ 6V: | 40 mA |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 700 mA |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 1.5 oz·in |
| Extended motor shaft?: | N |
| Motor type: | 0.7A stall @ 6V (MP 6V) |
No; the information we have available for this motor can be found on its product page. However, you can approximate various additional motor parameters from the information found in the “Specs” tab.
The electrical resistance of the motor can be approximated by dividing the rated voltage by the stall current (at the rated voltage). The electromotive force constant (Ke) can be approximated by dividing the rated voltage by the free-run speed (at the rated voltage). To approximate the motor torque constant (Kt), you can divide the stall torque by the stall current.
For pretty much any DC motor, the current, speed, power, and efficiency curves as a function of torque will look like those in the graph below (assuming motor voltage and temperature are constant):
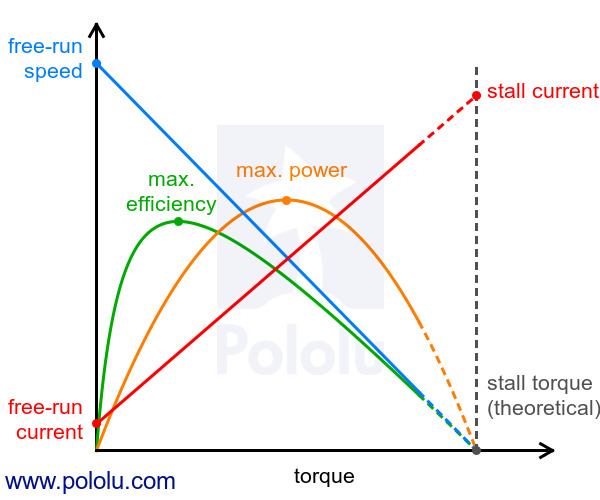 |
The current and speed curves are approximately linear, and the product pages for our motors provide the approximate end points for these lines: (0 torque, no-load current) and (stall torque, stall current) for the red line, and (0 torque, no-load speed) and (stall torque, 0 speed) for the blue line.
The orange output power curve is the product of the speed and the torque, which results in an inverted parabola with its peak at 50% of the stall torque.
The green efficiency curve is the output power divided by the input power, where the input power is current times voltage. The voltage is constant, so you can divide the output power curve by the current line to get the general shape of the efficiency curve, which in turn lets you identify the torque, speed, and current that correspond to max efficiency.
There are many programs out there that you can use to generate these curves. For example, if you have access to MATLAB, you can use this customer-created MATLAB script to generate these motor plots for you from the specifications we provide for each gearmotor.
Note: A good general rule of thumb is to keep the continuous load on a DC motor from exceeding approximately 20% to 30% of the stall torque. Stalling gearmotors can greatly decrease their lifetimes, occasionally resulting in immediate damage to the gearbox or thermal damage to the motor windings or brushes. Do not expect to be able to safely operate a brushed DC gearmotor all the way to stall. The safe operating range will depend on the specifics of the gearmotor itself.